Download "Fiction film financing in Europe: A sample analysis of films released in 2022" here
This new report finds that
- Direct public funding remained the single most important financing source of European theatrical fiction films, contributing 27% of the total financing volume. Production incentives remained for the second year in a row the second most important financing source, accounting for 20% of total financing volume. (The report defines direct public funding as public funding from national, regional and local bodies in the country of origin as well as from minority financing countries and supra-national sources. Production incentives include both national as well as foreign production incentives).
- The median average budget of a European theatrical live-action fiction film released / scheduled to be released in 2022 was EUR 2.19 million.
- Both average budgets as well as financing structures differ significantly between markets. In particular, the percentage share of direct public funding in film financing decreases with increasing market size and budget volume.
This annual report is the fruit of a major collaboration project between the European Audiovisual Observatory, part of the Council of Europe in Strasbourg, and the European Film Agency Research Network (EFARN). It aims at providing concrete figures on how European theatrical fiction films are being financed, offering a big-picture, pan-European perspective, and complementing work done at national levels.
Based on the actual budget analysis of 713 European live-action fiction films released / scheduled for release in 2022, this is probably the largest pan-European data sample available to date on the financing of European fiction films for this year. The report provides unique fact-based insights on a wide variety of research questions, from the quantification of the average budget of theatrical European fiction films, to the importance of individual financing sources.
Financing structure of European theatrical fiction films
In 2022, the financing of European theatrical fiction films continues to be primarily based on five different financing sources: direct public funding; production incentives; broadcaster investments; producer investments; and pre-sales (Broadcaster investments combine co-production investments by broadcasters with pre-sales made to broadcasters based in any of the co-producing countries. Pre-sales combine national and international pre-sales; pre-sales in the country of origin).
The single most important financing source was clearly direct public funding, which accounted for 27% of the total financing volume tracked in the analysis. Direct public funding was followed by production incentives which accounted for 20% of total financing while broadcaster investments accounted for 18% of total financing, slightly ahead of producer investments (excl. broadcasters) and pre-sales (excl. broadcasting rights) which accounted for 16% and 15% of total financing respectively. Other financing sources, including VOD investments, private equity, debt financing or in-kind investments are negligible from a cumulative perspective.
However, there appear to be significant structural differences among countries regarding how theatrical fiction films are financed. Some of these differences are apparently linked to market size. Two obvious differences concern direct public funding and production incentives. The data clearly suggests that the weight of direct public funding in film financing decreases with increasing market size and vice versa. While comprising only 19% of total financing in the four large sample markets, direct public funding accounted for 46% in medium-sized and 58% in small sample markets.
In contrast, the financing weight of production incentives seems to increase with market size, increasing from only 8% in small markets, to 14% in medium-sized markets up to 23% in large markets (24% excl. French films). Also, the significance of producer investments as well as pre-sales appears to be comparatively low in small and medium-sized markets when compared to large markets.
Breakdown of cumulative financing volume by source (2022)
Ranked by percentage share; based on all 482 sample films
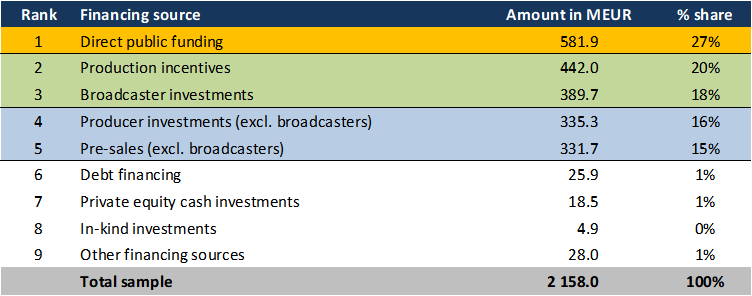
Source: European Audiovisual Observatory
Theatrical fiction budgets in Europe
The data sample studied [see methodological notes below] suggests that the mean budget of a European theatrical fiction film released in 2022 represented EUR 3.03 million while the median sample budget amounted to EUR 2.19 million.
However, average budgets differ widely among countries. Not surprisingly, average budgets are higher in larger markets and lower in countries with lower box-office potential, as exploitation in national markets remains key for most films. The median budget of a European fiction film originating in France, Germany, Italy, Poland or the UK (the large markets included in the sample) amounted to EUR 2.7 million in 2022 compared to EUR 1.9 million for fiction films produced in a medium-sized European market and EUR 0.9 million for fiction films from small markets.
Methodology
The analysis is based on a data sample comprising detailed financing plans for 713 European live-action fiction films - theatrically released / scheduled for release in 2022 from 24 European countries. The data sample includes both 100% national as well as European-majority-led co-productions. It covers a cumulative financing volume of EUR 2.16 billion. The data sample is estimated to cover 56% of the total number of European live-action fiction films released theatrically in 2022.
Definitions
Direct public funding includes public funding from national, regional and local bodies in the country of origin as well as from minority financing countries and supra-national sources.
Production incentives includes both national as well as foreign production incentives.
Broadcaster investments combine co-production investments by broadcasters with pre-sales made to broadcasters based in any of the co-producing countries.
Pre-sales combine national and international pre-sales; pre-sales in the country of origin.
